A True Tale of Two Ransomware Attacks
Read a true tale about two different schools and how they each recovered from a ransomware attack. As you read, you’ll learn how an effective backup plan and a well-thought-out business continuity strategy is a critical part of your cyber security efforts. The similarities between the schools is that both ransomware attacks were thought to be started by the click of a phishing emails. The difference is in their disaster recovery plans.
RANSOMWARE PREVENTION
A TALE OF TWO SCHOOLS
Imagine a world where ransomware didn’t exist. Now, snap back to reality and read a tale about two different schools and how they each recovered from a ransomware attack. As you read, you’ll learn how an effective backup plan and a well-thought-out business continuity strategy is a critical part of your cyber security efforts. The similarities between the schools is that both ransomware attacks were thought to be started by the click of a phishing email. The difference is in their disaster recovery plans.
The Allegheny Intermediate Unit School System, Pennsylvania, U.S.A.
School A, The Allegheny Intermediate Unit school system, DID NOT have to engage with the criminals and were able to use the services of a third-party to get their critical data recovered quickly. When you read the wording on various articles related to this incident, it appears that the school system quickly engaged with their cyber insurance carrier. Their insurance carrier mobilized resources quickly to identify and remediate the attack and then restored from existing backs of critical data. THIS is how the process is supposed to work.
The University of Maastricht, The Netherlands
School B, The University of Maastricht, did not have an adequate plan in place and had to completely shut down information systems and pay the ransom in order to decrypt their computers and servers. The timeline on this attack is interesting; the original compromise occurred a little over two months before their networks were ransomed. Had they had an extra layer of defense like the RealTime Cyber Defense package, they could have potentially caught the attack during this phase.
LESSONS LEARNED?
The lessons that a school [or any business] that has been through an event like this one will make them better at risk-based decisions going forward. Now they know that they are vulnerable to an attack like this and will take positive steps to introduce better prevention and detection processes.
Todd Swartzman, RealTime CISO
TODD’S TAKE ON THE RECOVERY:
After paying the ransom, it was pretty fast to decrypt that many systems and perhaps most were using the same decryption keys – some victims aren’t that lucky and have to juggle hundreds or thousands of decryption keys that really slows down recovery. Part of the decision to pay was based on how much quicker it can be to decrypt machines rather than reloading from scratch. The statement by the university indicates that they may not have had backups of some of their critical data.
summary:
Be sure to have a good backup in place;
Cyber insurance is a great idea;
Adding a cyber security plan could have helped detect the internal attack during the months they “inside” the system rather than waiting.
WANT TO TALK?
Want to talk to our Chief Information Security Officer about a better strategy for your business?
New Twist on an Office 365 Phishing Scam
You are probably familiar with the phishing scams that attempt to get you to share your Office 365 password with the criminals, via a fake Office 365 logon page. Well, there is a new twist you need to make everyone aware of in your organization.
PHISHING WITH OFFICE 365 SPOOFS
You are probably familiar with the phishing scams that attempt to get you to share your Office 365 password with the criminals, via a fake Office 365 logon page. Well, there is a new twist you need to make everyone aware of in your organization.
The lure used in this new phishing scam is nothing new; typical social engineering trying to get you to do something you should not do. What is unique is the method used to gain access to your Office 365 organization. Below we explain how the criminals are trying to get access to your information through Office 365.
This is the screen you will see when asked to login to Microsoft Office 365.
SPOT A SCAM
Like a lot of these scams, you’ll be presented with a logon page for Office 365 like this one (right), which is the right Microsoft Office 365 logon page, not a fake one:
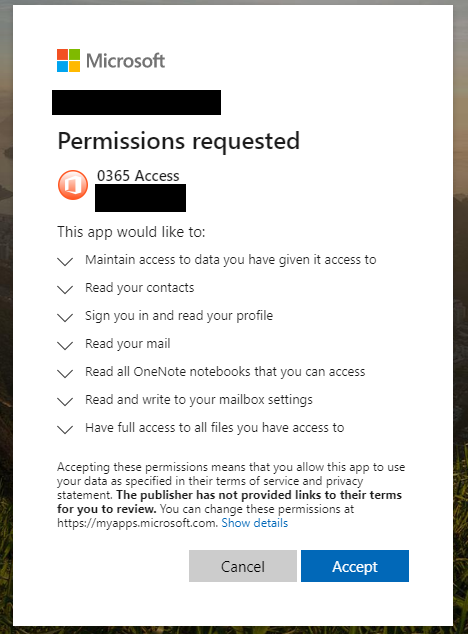
After you login, or if you were already logged into Office 365 (many people stay logged in), you’ll then see this permissions request pop up (image left). THIS IS THE BAD GUYS asking you to allow them access to everything in Office 365 account!!!
STAY ALERT
Careful attention to the things you are being asked to allow access to should trigger an alarm bell. While this is an actual function in Office 365 that has legitimate uses, if you are casually checking emails and this pops-up, immediately stop what you are doing and alert your cybersecurity team or IT department. This technique abuses the add-ins feature of office 365.
Currently, this phishing exploit appears to be coming in via spoofed sender emails with One Drive attachments. However, there is no reason that the delivery method won’t change to other techniques eventually. The emails are like traditional phishing emails, usually from a spoofed sender. Some email filters will probably catch these before anyone receives them. Security-aware people who know how to spot phishing messages probably won’t fall for this one if they stay alert!
4 Lessons From The Most Devastating Cyber Attack In History
Today’s history lesson comes from Wired, who did a really interesting piece last year on the Notpetya cyber attack that targeted the Ukraine, but led to billions of dollars in collateral damage. And really, the story isn't even really about Ukraine or other companies. The story is truly about a nation-state’s weapon of war that was released in such a medium that it knew no borders.
Today’s history lesson comes from Wired, who did a really interesting piece last year on the Notpetya cyber attack that targeted the Ukraine, but led to billions of dollars in collateral damage. And really, the story isn't even really about Ukraine or other companies. The story is truly about a nation-state’s weapon of war that was released in such a medium that it knew no borders. The collateral damage didn’t just affect it’s intended victim, but crossed over everywhere at once. It’s a warning to businesses like yours and mine to be prepared for the worst. You may not be the original intended target, but if you don’t take active precautions then you could easily be taken down like so many other companies and countries mentioned in the following story.
SUMMARY OF NOTPETYA CYBER ATTACK
For four or five years, Ukraine and Russia have been in an undeclared war that has killed more than 10,000 Ukranians. The conflict is so bad that Ukraine has become a testing ground for Russian cyberwar tactics. They have penetrated networks, hacked governmental organizations and companies as well as media outlets to railway firms. They’ve even gone as far as causing widespread power outages.
During this time unbeknownst to anyone, Russian military hackers hijacked Linkos Group company’s update servers to give them a hidden back door into the thousands of PCs around the country and the world. Then they waited…and in June 2017, the Russian saboteurs used the back door they had setup and released a piece of malware called NotPetya, their most vicious cyberweapon yet.
The code that the hackers pushed out was honed to spread automatically, rapidly, and indiscriminately.
“To date, it was simply the fastest-propagating piece of malware we’ve ever seen,” says Craig Williams, director of outreach at Cisco’s Talos division, one of the first security companies to reverse engineer and analyze NotPetya. “By the second you saw it, your data center was already gone.”
Within hours of its first appearance, the worm raced beyond Ukraine and out to countless machines around the world, from hospitals in Pennsylvania to a chocolate factory in Tasmania. It crippled multinational companies including Maersk, pharmaceutical giant Merck, FedEx’s European subsidiary TNT Express, French construction company Saint-Gobain, food producer Mondelēz, and manufacturer Reckitt Benckiser. In each case, it inflicted nine-figure costs. It even spread back to Russia, striking the state oil company Rosneft.
READ THE FULL STORY: https://www.wired.com/story/notpetya-cyberattack-ukraine-russia-code-crashed-the-world/
FOUR LESSONS FOR EVERY BUSINESS FROM NOTPETYA
A number of mistakes, oversights, and criminal acts went into making this attack successful. You’ll also no doubt want to take a look at how something similar might impact you and what steps you can take to protect yourself. There are a lot of takeaways in this story, but here are four very important ones that apply to every business that utilizes computers in running their business:
Enforce utilizing only approved software - Maersk would not have been impacted had ONE finance executive not installed an accounting application on his computer. This stresses the importance of creating and sticking to approved software lists within your organization. Now, this one may have been approved – the story doesn’t say, but in this interconnected world, one mistake can cost a lot.
Patch management of the operating systems and applications - Cyber criminals can infect computers that aren’t patched, and then grab the password from those computers to infect other computers that are patched. Patching was lackluster at best and was a known vulnerability that could have been corrected, but wasn’t.
Backups, backups, backups - Maersk got lucky by finding one domain controller that wasn’t infected as they had no backups – they depended on replicas saving their day, and in this case, I supposed it did, but only because of a power outage isolating one network out of hundreds.
Know your risks and have mitigation plans - Understand that you can do almost everything right and still be impacted – so understand your risks and have mitigation plans for your most critical processes.
Bonus – Vendor risk management. You can do everything right, but if the firms who provide your cloud applications, websites, even IT services are vulnerable, then you must understand that their risks are your risks. Be sure to include these vendors in your overall risk management program and see how they address their risks so you can make informed decisions.
CLOSING
RealTime specializes in helping businesses with complete technology solutions, backups, cyber protections and mitigation plans, vulnerability assessments and more. If you don’t have a plan in place, contact RealTime to begin the process of protecting your business. Feel free to contact us here or call us at (334) 678-1417.
SMB Cybersecurity Checklist (Part 1 of 3)
Given all the news regarding cyberattacks, it’s not hard to get businesses thinking about improving their cybersecurity. But, when those same businesses want to move beyond just thinking about improvement and act to really mature their security, they may feel like they are on their own. After all, the typical small business doesn’t usually have an IT staff, and probably doesn’t know where to begin this journey. Not to worry, we’re here to help.
Given all the news regarding cyberattacks, it’s not hard to get businesses thinking about improving their cybersecurity. But, when those same businesses want to move beyond just thinking about improvement and act to really mature their security, they may feel like they are on their own. After all, the typical small business doesn’t usually have an IT staff, and probably doesn’t know where to begin this journey. Not to worry, we’re here to help.
These are the first 5 things we recommend a small business (really any business) do as they work to improve their cybersecurity posture.
ONE
The very first thing we recommend is to have a plan. If you are not sure how to develop a plan, here is an overview of the different areas you’ll want to review as you begin the process of improving your cybersecurity: https://www.realtime-it.com/blog/solid-cybersecurity-plan.
TWO
You must perform risk and vulnerability assessments for your business. You want to understand (and document) how you use technology in your business and the technical risks you face so you can prioritize your cybersecurity improvement efforts. It is not possible to fix everything at once, and your risk assessment will help you identify what might be addressed easily and what is critical to address immediately.
For the rest of Part 1, we’ll skip ahead a bit in the process to shore up areas every business needs to address if they haven’t already.
THREE
Backups – air-gapped, tested, secured. Simply put, you want to regularly backup all your important data, and have a copy of that backup outside of the building and inaccessible from your local computers. This way, if something bad happens, the backup isn’t affected along with everything else. Don’t forget, you also want to periodically test your backups to make sure the process is working, and the data is up-to-date and usable.
FOUR
Firewall – managed, NextGen security. Your firewall, with the proper security services in force, is one of your primary means of cyber defense. Firewalls have been considered a security necessity for about twenty years now– and no, you can’t get a proper business-grade firewall off the shelf at your local big-box electronics store.
FIVE
Security Awareness Training – ongoing and often. If your staff is using computers and the internet, they need to be aware of the threats, to know what to watch for, and to understand how to report anything out of the ordinary. – We have a great blog on Security Awareness Training here with a lot of great links.
Finally, even though we said we’d only discuss the first five steps to consider in addressing stronger cybersecurity, we really want to make sure you understand how important it is for you to obtain adequate cyber insurance appropriate to your business type and cyber risks. Talk to your insurance agent and ask for qualified resources and options to help you find the best policy to meet your needs.
A How-To-Guide for Multi-Factor Authenticiation
Multifactor authentication (MFA) is defined as a security process that requires more than one method of authentication from independent sources to verify the user’s identity. In other words, a person wishing to use the system is given access only after providing two or more pieces of information which uniquely identifies that person.